Service hotline
+86 0755-83975897
Release date:2021-12-28Author source:KinghelmViews:1870
Goodbye, 2G!
On May 25, 2021, the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT officially announced the approval of operator LG U+'s application to close 2G services. Following the closure of 2G services by KT and SKT, two other mobile operators in South Korea in January 2012 and July 2020, LG U+ will terminate 2G services by the end of June 2021.

Turn off 2G service
This marks that the 25-year-old 2G (CDMA) in South Korea has finally come to an end and will completely bid farewell to the historical stage.
Hello, 5G!
In May 2021, the Korean Ministry of Science and Information and Communication Technology released the latest statistics showing that since 5G commercialization in April 2019, South Korea's 5G network traffic surpassed 4G for the first time.
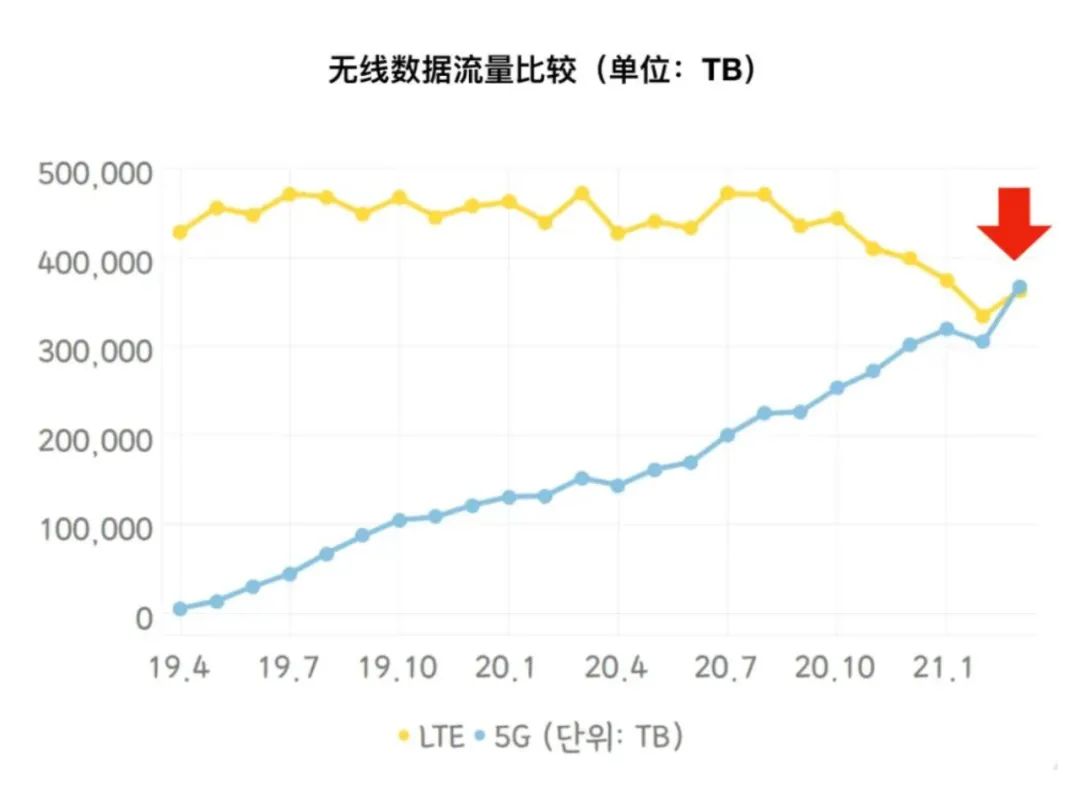
The data shows that in March 2021, the total data traffic generated by South Korea's 5G network was 368,025TB, slightly higher than the 363,301TB of the 4G network. At the same time, with the continuous increase of 5G network traffic, South Korea's 4G network traffic shows a gradual downward trend.
This marks that South Korea has truly entered the 5G era.
a chronometabolic curtain
Speaking of the history of 2G in South Korea, let's talk about the history of South Korea's telecommunications reform. Similar to the history of my country's telecommunications industry, in the 1980s, that is, in the 1G era, Korea Mobile Telecommunications (KMT), a subsidiary of the state-owned enterprise Korea Telecom, exclusively managed Korea Mobile Telecommunications. In order to accelerate the popularization of mobile services, South Korea began to privatize the telecommunications industry and lowered the barriers to entry for telecommunications to introduce competition. After this round of restructuring, the Korean telecommunications market has emerged as a competition among five mobile operators, SK Telecom, Shinsegi Telecom, KT Freetel, Hansol PCS, and LG Telecom. Then into the 21st century, after a series of mergers, the current pattern of competition among the three mobile operators SKT, KT and LG U+ has been formed. Among them, KT Freetel and LG Telecom can be regarded as the predecessors of the current KT and LG U+.
In the 1990s, at the time of the transition from 1G to 2G, when the attention of most regions and manufacturers in the world was focused on the GSM standard proposed by Europe, South Korea took a different approach and chose the GSM standard that was relatively backward in commercial maturity. CDMA technology. In January 1996, Korea Mobile Communications (the predecessor of SKT) launched the world's first 800MHz-based CDMA IS-95A service in Seoul. Subsequently, operators such as KT Freetel and LG Telecom launched PCS (1800MHz) based CDMA services.
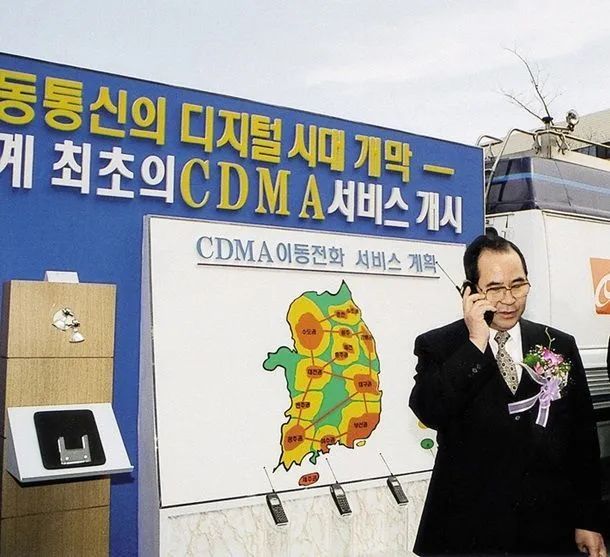

It is against this background that the fierce market competition environment has promoted the rapid development of the CDMA business in South Korea. In August 1998, South Korea achieved the world's first IS-95B service with the highest transmission rate of 114Kbps. In October 2000, the world's first commercial CDMA2000 1X. In January 2002, South Korea was the first in the world to commercialize CDMA2000 1X EV-DO, with a data transmission rate of up to 2.4Mbps. According to statistics, before the commercial use of CDMA, the total number of mobile communication users in South Korea was 1.5 million, and in 2000 this number reached 27 million, an increase of 15 times.
It can be said that in the 2G era, South Korea created the myth of CDMA. Thanks to the bold introduction of CDMA, South Korea has gradually transformed from an importer of mobile communication equipment and terminals to a major exporter in the 2G era, becoming a leading country in global mobile communication technology, and has also achieved South Korea's telecom equipment represented by Samsung and LG. And terminal manufacturers have sprung up. It is no exaggeration to say that South Korea's CDMA saved Qualcomm and made the South Korean communications industry. The Korean industry generally believes that CDMA is the basis for the rise of the Korean communication industry. Based on this, South Korea has gradually become a telecom power, and has continued to promote 3G, 4G and 5G leadership.
However, entering the 3G/4G era, as the disadvantage of CDMA in technological evolution gradually emerged, the successful Korean 2G CDMA also began to go downhill in history. Entering the 3G era, SKT and KT chose WCDMA technology, and then gradually migrated 2G CDMA users to 3G WCDMA. Entering the 4G era, due to the lack of spectrum resources, in order to re-cultivate the 2G frequency band for 4G LTE, KT was the first to obtain the approval of the Ministry of Science and Information and Communication Technology of South Korea, and announced the termination of 2G service in early 2012. Due to relatively abundant spectrum resources, SKT officially terminated 2G services in July 2020.
For KT and SKT to terminate 2G services, both operators have faced opposition from the Korean public and media, but the Korean Ministry of Science and Information and Communication Technology believes that 2G CDMA equipment has been running for more than 20 years, and the aging of equipment has led to frequent failures and spare parts. Insufficient, in turn, renders the equipment irreparable, has a high risk of failure, and is quite expensive to maintain, making it unsuitable for continued operation. On the other hand, from the perspective of spectrum utilization, the number of 2G users in South Korea only accounted for about 1% of the total number of mobile users at that time, and South Korea’s CDMA occupied the 800MHz and 1800MHz golden frequency bands. If the 2G network is not closed, it is indeed too wasteful of spectrum resources.

2G CDMA mobile phone
LG U+ is the only Korean mobile operator that did not introduce WCDMA technology in the 3G era. It adopted the EV-DO Rev.A/B technology based on CDMA2000, which is equivalent to a direct transition from 2.5G to 4G LTE, which is exactly what it is. The reason for the delay in getting approval to shut down the 2G network. Although the number of 2G subscribers of LG U+ was only around 370,000 by November 2020 (this number will decrease to 140,000 by May 2021, accounting for only 0.82% of the total number of LG U+ mobile subscribers), Korea Science and Information Communication The technical department believes that LG U+ has been upgraded based on CDMA technology, has a long operation time, and has relatively new network equipment. In addition, after SKT shuts down 2G services, LG U+ still has to bear some 2G users who have transferred SKT's numbers. U+ was determined to be the last operator in South Korea to close 2G services, and it was not until May 25, 2021 that LG U+ was officially approved to close 2G services.
Since then, South Korea's 2G has officially announced a complete curtain call after 25 years of history!
an era begins
On the afternoon of April 3, 2019, a tense atmosphere filled the conference room of the South Korean Ministry of Science and ICT. Executives from South Korea's three major carriers and Samsung Electronics are holding an emergency meeting with government officials in charge of communications. Just a few hours ago, they received an important piece of information that the US operator Verizon will commercialize 5G on April 4, which is a week earlier than its original plan on April 11.
The three major operators in South Korea originally planned to commercialize 5G on April 5, but now Verizon has advanced the commercial time of 5G, which means that South Korea will lose the title of "the world's first commercial 5G". As a result, the South Korean government and the three major operators and Samsung Electronics convened this meeting urgently, and finally discussed and decided to advance the 5G commercial time to 23:00 on April 3 to regain the title of "world number one".
In this way, at 23:00 on April 3, 2019, just one hour ahead of Verizon, South Korea's 5G was officially announced for commercial use.

Today, South Korea's 5G has been commercialized for two years and one month. What kind of achievements has South Korea's 5G achieved?
First of all, from the perspective of operators, 5G has indeed driven the revenue and profit growth of Korean operators. Not long ago, the Korean media described the performance of the three major Korean operators in the first quarter of 2021 as "surprising". In the first quarter of 2021, LG U+ sales were 3.41 trillion won, operating profit was 275.6 billion won, an increase of 4% and 25.4% year-on-year, respectively, and operating profit hit a new high since 5G commercialization; KT's comprehensive sales were 6.294 Trillion won, operating profit was 444.2 billion won, an increase of 3.4% and 15.4% year-on-year, respectively; SKT's consolidated sales and operating profit were 4.78 trillion won and 388.8 billion won, respectively, an increase of 7.4% and 29% year-on-year. The total operating profit of the three major operators has reached a new high since the commercial use of 5G. According to the analysis, new services centered on content have grown significantly.
Secondly, from the perspective of industrial ecology, South Korea's 5G first-mover advantage has driven the development of South Korea's entire industrial chain. For example, according to the latest statistics from market research firm Dell'Oro, Samsung accounts for about 7.2% of the global 5G equipment market share, and has become the world's fifth largest 5G equipment supplier after Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia and ZTE. Breakthrough; South Korea's KMW has not only turned losses into profits in the 5G era, but also has seen a significant increase in both turnover and profits after experiencing continuous losses through OEM and RF device provision. In addition, thanks to the successful commercial experience of 5G, Korean operators are also actively exporting 5G network construction consulting services and immersive content solutions to overseas operators. For example, SKT cooperated with Deutsche Telekom to establish a strategic alliance to export network construction design to Deutsche Telekom and transmission-related technologies to help Deutsche Telekom accelerate 5G commercialization; KT provides 5G network design consulting services to operators in Vietnam, Saudi Arabia and other countries; LG U+ signed a 5G VR content export contract with Hong Kong Telecom, etc.

According to the latest data from the Korean Ministry of Science and Information and Communication Technology, as of the end of April, the number of 5G terminal users in South Korea reached 15.15 million, which is the first time that the number of 5G users has exceeded 1,500 since the commercial use on April 3, 2019 for about two years and one month. Ten thousand. Although these 15 million 5G users only account for 21.2% of the total number of mobile users in South Korea, it is worth noting that the total mobile data traffic contributed by these 21.2% of 5G users has exceeded 4G. The data shows that in March 2021, the total data traffic generated by South Korea's 5G network was 368,025TB, slightly higher than the 363,301TB of the 4G network. At the same time, on the other side of the escalating 5G network traffic, 4G network traffic showed a gradual downward trend after hitting a record high in March 2020 (470,000TB in a single month).
On the one hand, 5G traffic surpasses 4G, and on the other hand, 4G traffic gradually declines. It is not difficult to see that South Korea has truly entered the 5G era.
An era has ended, an era has come. Goodbye, 2G! Goodbye, CDMA! Hello, 5G!
This content comes from the network/netyou mercenary. This website only provides reprints. The opinions, positions, technology, etc. of this article have nothing to do with this website. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it!










Copyright © Shenzhen Kinghelm Electronics Co., Ltd. all rights reservedYue ICP Bei No. 17113853